

Sodium polyacrylate
| Chemical name£ºpolyacrylate sodium (PAAS) English name£ºsodium polyacrylate molecular structure£º¡ª[-CH2CHCOONa-]¡ª 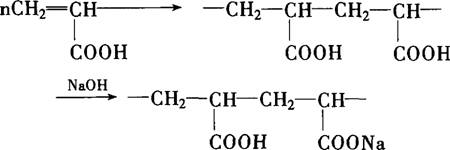 PAAS is a polysnion macromolecule dielectric£¬which is an important widely used chemical product developed in modern times. It is also widely used in such field as ?environmental protection¡¢food¡¢medicine¡¢textile¡¢water processing¡¢petrochemistry ¡¢metallurgy etc. |
|
¡¾character¡¿ white powder ,colorless and tasteless . It has a strong characteristic of absorbing moisture. It is a high molecular compound both has hydrophilia and drainage radical. It can be dissolved in water to become extremely thick transparent liquid. The viscosity of 0.5% solution is about 1 Pa¡¤s£¬which is nearly equal to CMC. It is 15-20 times as big as sodium alqinate. Heating, neutral salt and organic acid are all have little effect on it. The viscosity will be increased under the condition of basic environment. It cannot be dissolved in organic solution such as ethanol and acetone. It cannot be decomposed when heated at 300¡æ.There is little change after a long period of preservation. Moreover, it is not easy to be decayed. It will form insolubility salt when meeting metallic ion that is more than bivalence (such as aluminum, lead, iron, calcium, magnesium and zinc.), which will arouse molecule cross linked and solidified sedimentation. When PH value is under 4, PAAS will produce sedimentation. |
| The application and function of PAAS: |
£¨I£©food processing |
|
|
PAAS enterprise standard
item \ standard |
food |
appearance |
White powder |
Free alkali |
qulified |
sulfate(SO4) |
¡Ü0.48% |
Loss in weight on drying |
¡Ü10% |
Residue on ignition |
¡Ü75% |
Heavy metal£¨ÒÔPb¼Æ£© |
¡Ü20ug/g |
arsenic (As2O3) |
¡Ü2ug/g |
Residual monomer |
¡Ü1% |
Lower polymer£¨lower than 1000degree of polymerization£© |
¡Ü5% |